The transition to renewable energy has made large-scale energy storage a cornerstone of modern power grids. These systems play a vital role in balancing supply and demand, integrating renewable energy, and ensuring grid stability. This article explores the types of large-scale energy storage, compares their features, and highlights Sungrow’s innovative utility storage solutions.

What is Large-Scale Energy Storage?
Large-scale energy storage refers to systems capable of storing vast amounts of energy for grid applications. These systems enable the storage of surplus energy during low-demand periods and its discharge during peak demand. This function is critical for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar into the grid while maintaining reliability and stability.
Major Types of Large-Scale Energy Storage
1. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Battery storage is among the most versatile and widely adopted solutions. Lithium-ion batteries dominate due to their high energy density and efficiency. Emerging technologies, such as solid-state and sodium-sulfur batteries, provide enhanced safety and durability.
Grid balancing to meet demand fluctuations.
Renewable energy integration by storing solar and wind power.
Commercial backup power for critical infrastructure.
2. Mechanical Storage
These systems store energy in physical forms.
Pumped Hydro Storage:
Uses gravity to store energy by pumping water to a higher elevation, releasing it to generate electricity when needed.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES):
Compresses air in underground caverns during off-peak hours and releases it to generate power.
Flywheel Energy Storage:
Converts electrical energy to rotational energy, offering quick response and high efficiency for short-term storage.
3. Thermal Energy Storage
These systems store heat or cold to produce energy later.
4. Chemical Energy Storage
Chemical storage, such as hydrogen energy, offers long-duration storage solutions. It converts electricity into hydrogen through electrolysis, which can be stored and converted back into electricity or used as fuel.
Comparison of Storage Types
Type | Advantages | Limitations | Key Applications |
Battery (BESS) | High efficiency, fast response, modular design | Limited lifespan, high upfront costs | Grid balancing, renewable integration |
Mechanical | Long lifespan, large capacity | Location-dependent, slow response | Long-term storage, peak shaving |
Thermal | Cost-effective for specific use cases | Limited to heat-based systems | Solar power plants, industrial heating |
Chemical | Long-duration storage, versatility | High costs, low efficiency | Seasonal storage, hydrogen fuel production |
Why Battery Energy Storage is Gaining Popularity
Battery energy storage systems are becoming mainstream due to their flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. BESS excels in applications like grid stability, renewable energy storage, and backup power for industries. Their modularity allows adaptation to various project sizes, making them a go-to solution for modern energy needs.
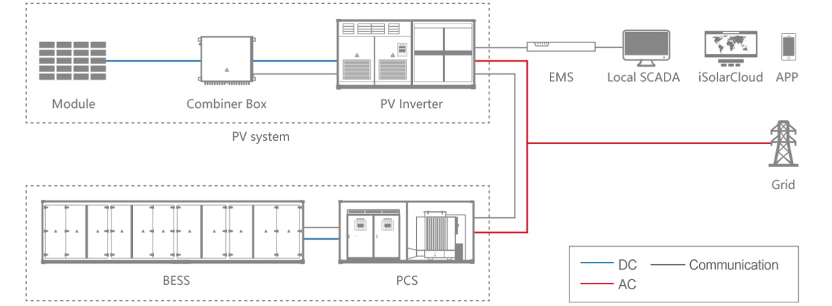
Sungrow’s Battery Energy Storage Solutions for Utility
Sungrow offers advanced utility-scale energy storage systems. These solutions are designed to meet the needs of large-scale projects with features that enhance performance, reliability, and efficiency.
Core Features:
Integrated and Modular Design: Compact systems combining batteries, inverters, and management software, with modular scalability for projects of different sizes.
High Efficiency and Reliability: Advanced power electronics optimize energy conversion, reducing costs and ensuring reliable, long-term operation.
Adaptability: Designed for grid services like frequency regulation and load shifting, with durability in extreme climates.
Smart Energy Management: Intelligent monitoring and real-time analytics enable precise control and fast grid response.
Conclusion
Large-scale energy storage is essential for the transition to a sustainable energy future. Battery energy storage systems, particularly those offered by industry leaders like Sungrow, are driving this transformation. With their high efficiency, adaptability, and intelligent management capabilities, Sungrow’s solutions meet the evolving needs of utilities and large-scale energy consumers.
As the world moves toward a cleaner energy future, innovative storage systems will continue to play a pivotal role in enabling reliable and sustainable power grids.